Derivative of y = xlnx xCalculus Calculus questions and answers Find all the first and secondorder partial derivatives of z (x, y) = x ln (2) sin (5y) au Use the Chain Rule to find aw and ᎧᎾ given w = 22 Vinya, = r2, y = cos (6), z = 44re Find using partial derivatives for xey ye" – 2x²y = 0Question 1 What Is The Derivative Of Y = X Ln X − X ?

Logarithmic Differentiation Ppt Download
Y=x^ln x derivative
Y=x^ln x derivative-I'll assume that you want to compute the derivative of mathy/x/math with respect to mathx,/math and that mathy/math is a function of mathx/math Use the quotient rule which in general says that math\displaystyle\left(\fracDerivative of 9/ln(x) Simple step by step solution, to learn Simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework Below you can find the full step by step solution for you problem We hope it will be very helpful for you and it will help you to understand the solving process




Derivative Of Logₐx For Any Positive Base A 1 Video Khan Academy
What is the derivative of y = x ln x − x ?Calculus Differentiating Logarithmic Functions Differentiating Logarithmic Functions with Base e 1 Answer Jim H Rewrite as #y = e^ln(x^lnx) = e^(lnxlnx) = e^((lnx)^2)# Explanation Now differentiateDerivatives Integrals Limits Algebra Calculator Trigonometry Calculator Calculus Calculator Matrix Calculator Solve algebra trigonometry statistics calculus matrices variables list Solve for y y=x\ln(x),x>0 y = x ln (x), x > 0 Graph Quiz Algebra 5 problems similar to y=x \times \ln ( x ) y = x
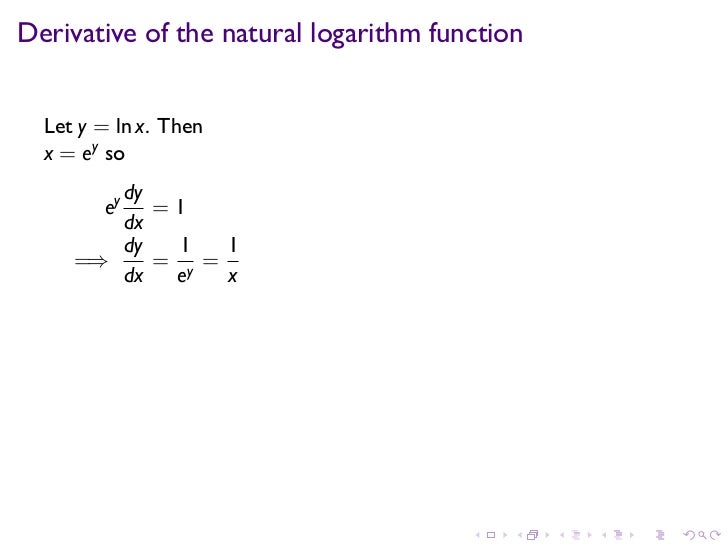
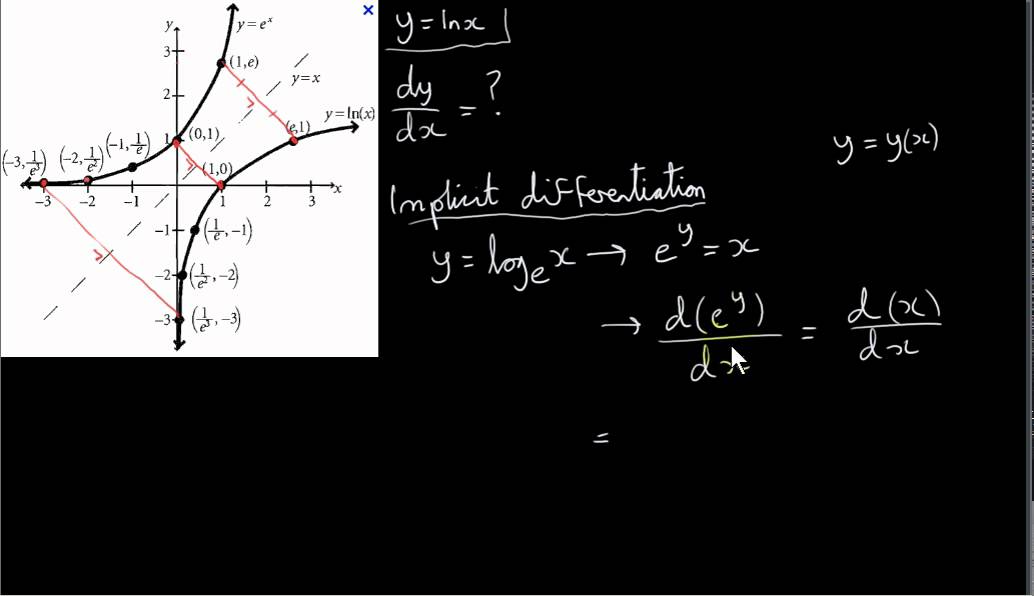
We know d/dx (e^x) = e^x*( log (e ) to the base e ), ie d/dx(e^x) = e^x* ln e = e^x ( as ln e = 1), similarly, for any arbitrary base a d/dx (a^x) = a^x*( log (a) to the base e) => d/dx (a^x) = a^x *ln(a) But the convention dealing this type ofY = ln x then e y = x Now implicitly take the derivative of both sides with respect to x remembering to multiply by dy/dx on the left hand side since it is given in terms of y not x e y dy/dx = 1 From the inverse definition, we can substitute x in for e y to get x dy/dx = 1 Finally, divide by x to get dy/dx = 1/x We have proven thePartial derivative of y^xln (x^3y6x) \square!
y = x/ln (x) Locate any relative extrema and points of inflection Extrema can only occur at critical points, or where the first derivative is zero or fails to exist Note that the domain for the function is x>0, x ne 1 y'= (lnx1)/ (lnx)^2 This function is defined for all x in the domain so we set it equal to zeroDerivatives implicitdifferentiation Share edited Nov 12 '14 at 056 Felix MarinFree derivative calculator differentiate functions with all the steps Type in any function derivative to get the solution, steps and graph
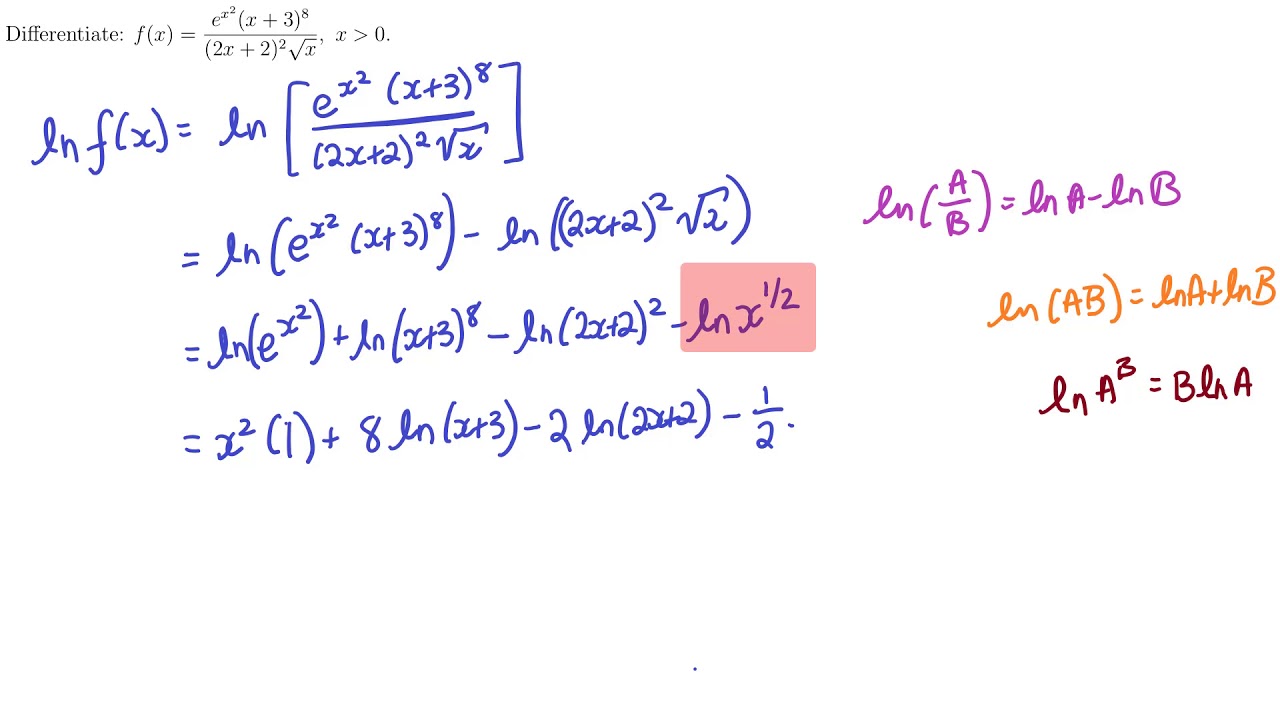



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



1
Derivatives › Second Derivative Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Mean, Median & Mode Scientific Notation Arithmetics AlgebraGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us! Active Oldest Votes 1 So if we use implicit differentiation eydy dx = 2ln(x)xln ( x) − 1 But ey = xln ( x), so dy dx = 2ln(x)xln ( x) − 1 xln ( x) = 2ln(x) x So you are quite right in your answer (and your approach is absolutely fine too!) Share answered Feb 16 '17 at 911



Derivative Of Ln X Youtube
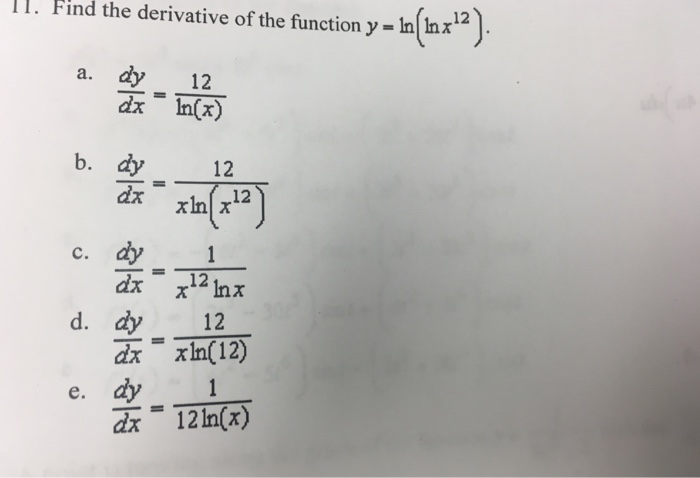



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Ln Ln X 12 Chegg Com
A partial derivative of a function is nothing but its derivative with respect to specific variables Since the question has not mentioned anything specific, I am just going to differentiate it with respect to mathx/math and mathy/math sepaFind the derivative of y = (x 2 1) 10 10 x 2 1 Solution dy dx = 10(2 x)(x 2 1) 9 d dx (10 x 2 1) = (x 2 1) 9 2 x 10 x 2 1 ln 10 842 Derivative of e x Since ln 2 < 1 and ln 4 > 1, then by intermediate value theorem ∃ a number between 2 and 4 such whose natural logarithm is equal to 1About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation



Derivative Of Lnx Natural Log Calculus Help Wyzant Lessons
(dy)/(dx) = 1/(xlnx) d/dx ln f(x) = ( f'(x) ) / f(x) => d/dx( ln ( ln x ) ) = (d/dx( lnx )) /lnx = (1/x)/lnx 1/( xlnx )Differentiate x^(lnx) using implicit differentiation and the chain ruleVideo by Tiago Hands (https//wwwinstagramcom/tiago_hands/)Extra Instagram Resource 3 Answers3 Use implicit differentiation, logs, and exponentials You can get rid of either xy or yx by using xy − yx = 1 Let f(x) = xy Then log(f(x)) = ylog(x) Then we take the derivative of both sides 1 f(x) df dx = dy dxlog(x) y x, and df dx = xy(dy dxlog(x) y x) Let g(x) = yx Then log(g(x)) = xlog(y)




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More




Ppt Section 3 5 Find The Derivative Of G X X 2 Ln X You Will Need To Use The Product Rule Powerpoint Presentation Id
Given y = xln(x) y = x ln ( x) We shall use the product rule of differentiation (f ⋅g)′ = f′gg′f ( f ⋅ g) ′ = f ′ g g ′ f y′ = lnxx 1 x = 1lnx y ′ = ln xSubstituting `y = x^(ln x) ` gives `dy/dx` = `2*ln x*x^(ln x)*(1/x)` = `2*ln x*x^(ln x 1)` The required derivative of `y = x^(ln x)` is `dy/dx = 2*ln x*x^(ln x 1)` Approved by eNotes EditorialAln X 1 Bx Ln X Cln X − 1 Dln X 2 This problem has been solved!




The Derivative Of Lnx And Examples Mathbootcamps
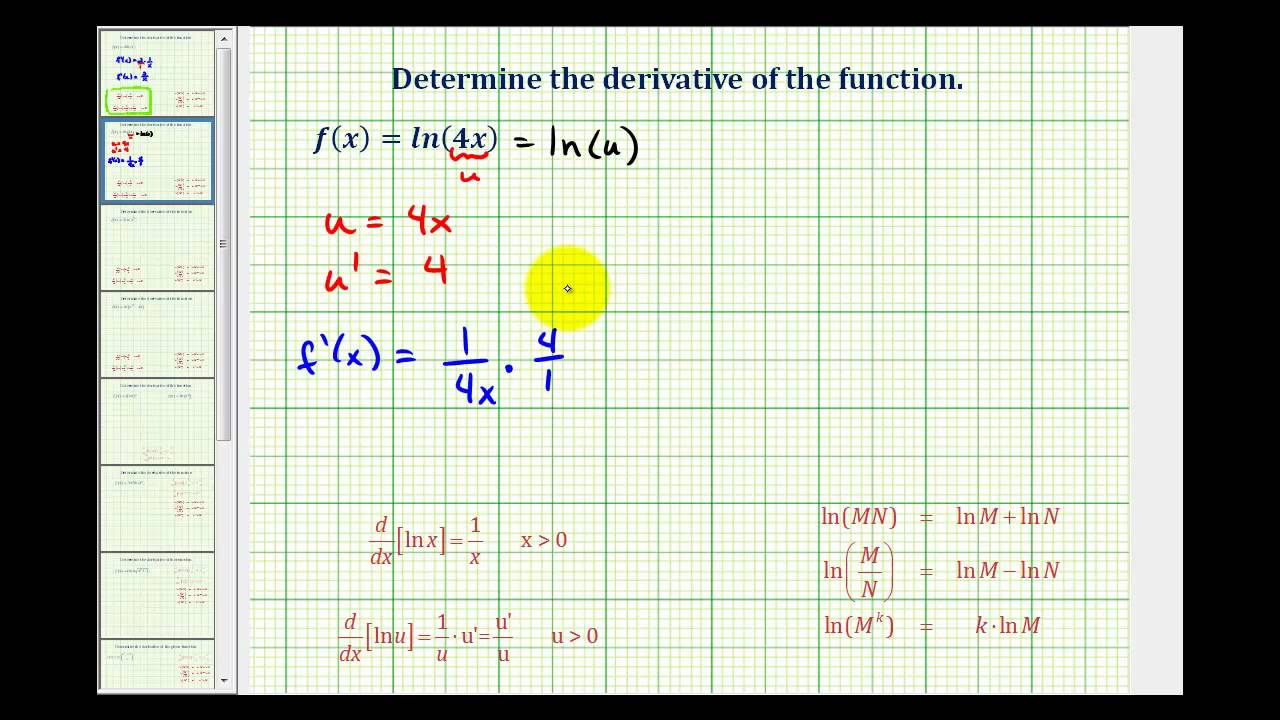



Calculus Derivative Of The Natural Log Ln Video Lessons Examples Solutions
Ln6x is loge (6x) A general rule of thumb I follow when differentiating natural logs (log e) is that whatever is inside the bracket is a function so f(x), in this case f(x)=6x The derivative of any natural log is (f'(x))/(f(x)) so in this case si(i) Let y=x^x, and take logarithms of both sides of this equation ln(y)=ln(x^x) Using properties of logarithmic functions, we can rewrite this as ln(y)=xln(x) Then differentiating both sides with respect to x, and using the chain rule on the LHS and product rule on the RHS, gives 1/ydy/dx=ln(x)1Answer to Find the derivative y = ln(x 3) By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions You can
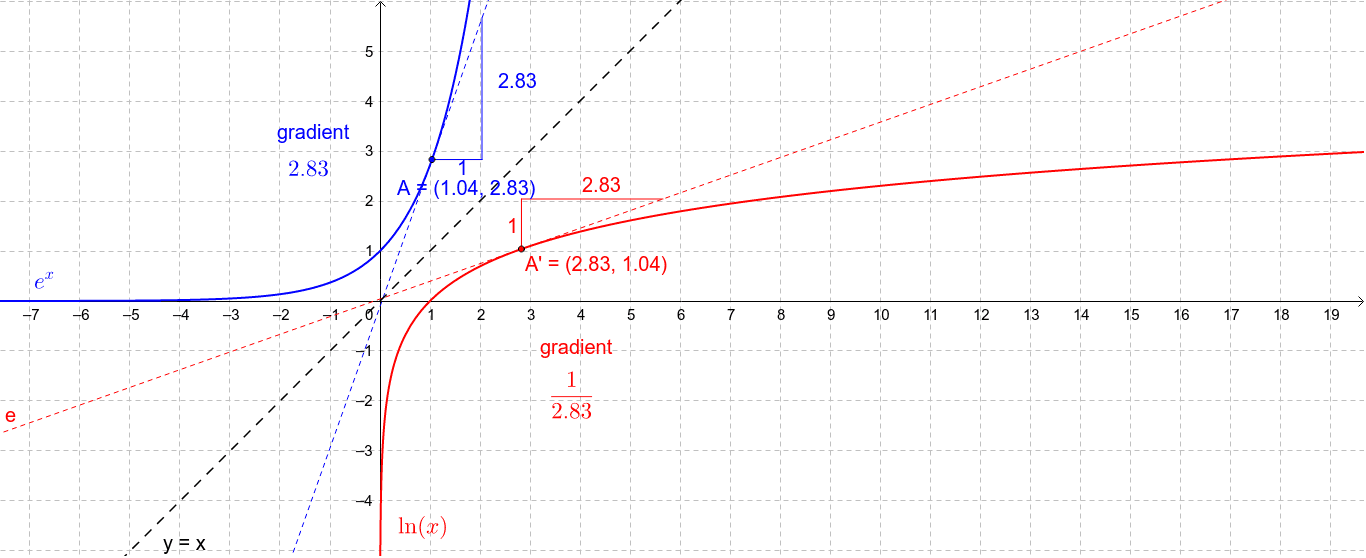



Derivative Of Natural Log Y Ln X Geogebra



At0wbebfqjhzjm
X y 1 = ln(x^16 y^2), (1, 0) y = Find the indefinite integral (Remember to use absolute values where appropriate) Question Find the derivative of th functionGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!Calculus Find the Derivative d/dx y = square root of x natural log of x y = √xln (x) y = x ln ( x) Rewrite √x x as x1 2 x 1 2 d dx x1 2 ln(x) d d x x 1 2 ln ( x) Differentiate using the Product Rule which states that d dxf (x)g(x) d d x f ( x) g ( x) is f (x) d dxg(x)g(x) d dx f (x) f ( x) d d x g ( x) g ( x) d d x



What Is The Differentiation Of Ln X And Log X Quora




5 Derivatives To Excel In Your Machine Learning Interview By Ester Hlav Towards Data Science
Integral of ln (x) \square!Second derivative of x^2*ln(2x), Full playlist https//wwwyoutubecom/playlist?list=PLj7p5OoL6vGzLwDjpT3gOA1K3RwUo8jDIf you enjoy my videos, then you canAnswer and Explanation Given y(x) =ln(x59) y ( x) = ln ( x 5 9) Differentiate the given function with respect to x x using the chain rule of differentiation, d dx (f(g(x)) = d dx f(g(x




Lesson 16 Derivatives Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions




Derivative Of Ln X Lnx 2 1 Lnx More
Answer to Find the derivative of y = x \\ln(x) x By signing up, you'll get thousands of stepbystep solutions to your homework questions YouThe derivative of y = xln (x) with respect to x is dy/dx = ln (x) 1 This result can be obtained by using the product rule and the wellknown results d (ln (x))/dx = 1/x and dx/dx = 1 The product rule of differentiation states that the derivative of a product of two functions f (x) and g (x) is given by f (x)g How do you find the derivative of #y = x^(ln x)#?



Search Q Derivative Of Ln 2x Tbm Isch



7clfy1ejzyygzm
You'll get y' = (e^x)' * (ln x) (e^x) * (ln x') If you simplify this using derivative rules, you'll get y' = (e^x * 1) * (ln x) (e^x) * (1/x)Find the Derivative d/dy e^(x/y) Differentiate using the chain rule, which states that is where and Tap for more steps To apply the Chain Rule, set as Differentiate using the Exponential Rule which states that is where = Replace all occurrences of with DifferentiateA ln x 1 b x ln x c ln x − 1 d ln x Expert Answer Previous question Next question Get more help from Chegg Solve it with our calculus problem solver and calculator
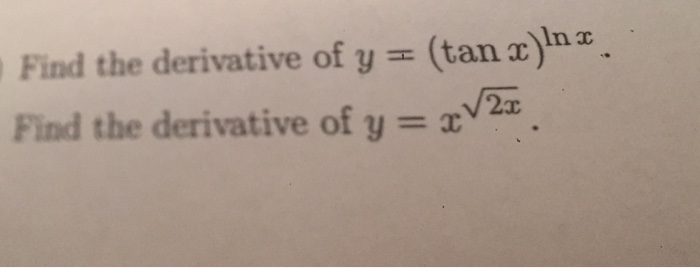



Find The Derivative Of Y Tan X Ln X Find The Chegg Com
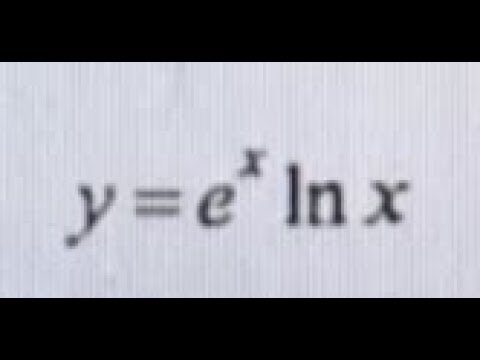



Y E X Lnx Find The Derivative Youtube
Derivative of ln(11/x), two ways, calculus 1 derivative example, how to take the derivative, logarithmic derivative, blackpenredpen, math for fun, https//tI know the answer to that is ln ( x) ln ( x), but how does the x go away ?Let, y = a^x Taking logarithm on bothsideboth side ln(y)=x * ln(a) Differentiating both side wrt x d/dx{ln(y)} =d/dx{x*ln(a)} (1/y)dy/dx = x*0 ln(a)*1=ln(a) dy/dx = y*ln(a) = a^x * ln(a)



Find The Derivative Of Y With Respect To X Y Ln Chegg Com




Find The Derivative Of Each Function A H X Chegg Com
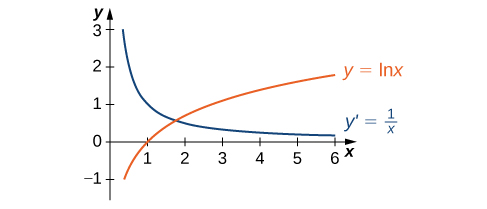
Derivative of the Logarithm Function y = ln x The derivative of the logarithmic function y = ln x is given by `d/(dx)(ln\ x)=1/x` You will see it written in a few other ways as well The following are equivalent `d/(dx)log_ex=1/x` If y = ln x, then `(dy)/(dx)=1/x`Examples) Find the derivative of the following expressions 1) y x = ln 4 2) y x = % ln 2 3 3) y x x = % ln 3 5 8 2 4) y x = ln You now have 5 sets of rules power, product, quotient, trig (6 rules), and now "ln" Just because there is an "ln"Consequently, the derivative of the logarithmic function has the form (logax)′ = 1 x logae By the changeofbase formula for logarithms, we have logae = lne lna = 1 lna Thus, y′(x) = (logax)′ = 1 xlna If a = e, we obtain the natural logarithm the derivative of which is expressed by the formula (lnx)′ = 1 x
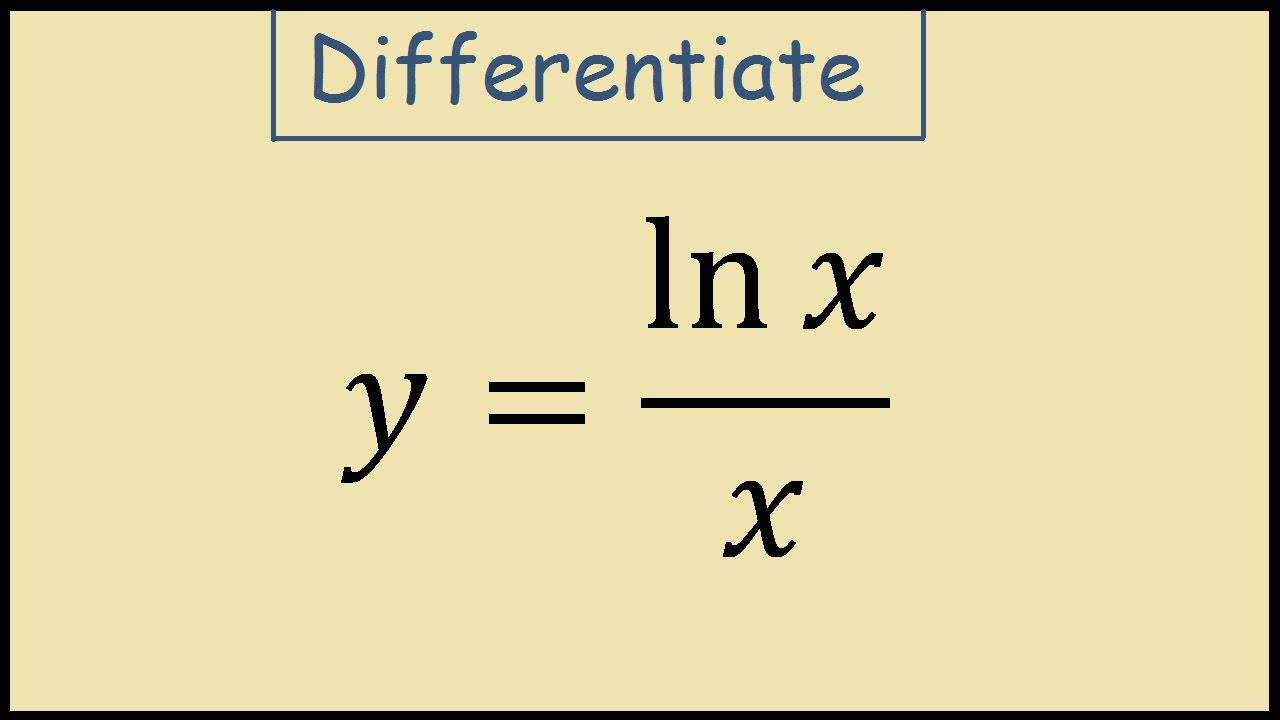



How To Differentiate Ln X X Youtube




Differentiate Y Ln X 3 Youtube
Y = d d x x ln x Take the derivative of both sides of the equation 1 y d y d x = x ⋅ 1 x ln x ⋅ 1 Apply the product rule, d ( u v) = u d v v d u 1 y d y d x = 1 ln What Is a Derivative of Xlnx?Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more



Implicit And Logarithmic Differentiation




Differentiate With Respect To X I Y Xlnx Ii Y X
9 #1 I am working on a homework problem which asks for the derivative of y = (tan x)^ ln x My strategy is to take the natural log of both sides which gives me ln y = ln (x) *ln (tan x) , after bringing down the ln (x) From here I am using implicit differentiation and the "product rule" and then plugging the original (tan x




Derivative Of Logₐx For Any Positive Base A 1 Video Khan Academy



Derivative Of Ln X X Youtube




Derivative Of Ln X From Derivative Of 𝑒ˣ And Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy




Y Ln X In X Explain Why Formula 5 Cannot Be Chegg Com




Worked Example Derivative Of Ln X Using The Chain Rule Video Khan Academy



Q Tbn And9gcq9arl5ab K Kkztqdma6czzlslnfprp6ljv7o6a18 5qqda4yy Usqp Cau




Derivative Of Ln X Video Khan Academy



3




Logarithmic Differentiation Ppt Download



3 9 Derivatives Of Exponential And Logarithmic Functions Calculus Volume 1



Derivative Of Xln X Youtube




Consider The Function F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 3 Compute The Partial Derivatives Of The First And Second Order Mathematics Stack Exchange



Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find The Chegg Com



Derivative Of Ln X Video Khan Academy



Use Logarithm C Differentiation To Find The Chegg Com




Find Y For Ln X Y Arctan Xy Mathematics Stack Exchange



What Is The Integrating Factor Of Math X Ln X Dy Dx Y 2 Ln X Math Quora




What Is The Differentiation Of Y Ln X With Respect To X Where Represents Modulus Function Quora




Answered 54 Y Ln X Cos Cos X 3d Bartleby



Derivative Of Y Ln X Geogebra
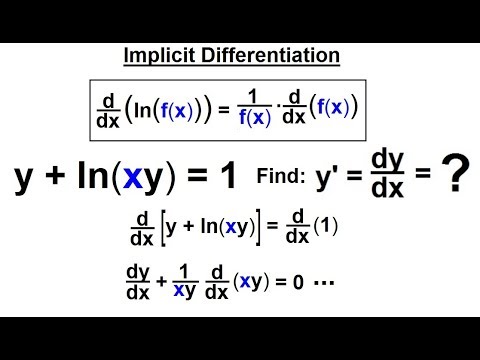



Calculus 1 Ch 5 1 Derivative Of E X And Lnx 19 Of 24 What Is Implicit Differentiation Youtube




Find The Derivative Of Y X Lnx Secx 3x
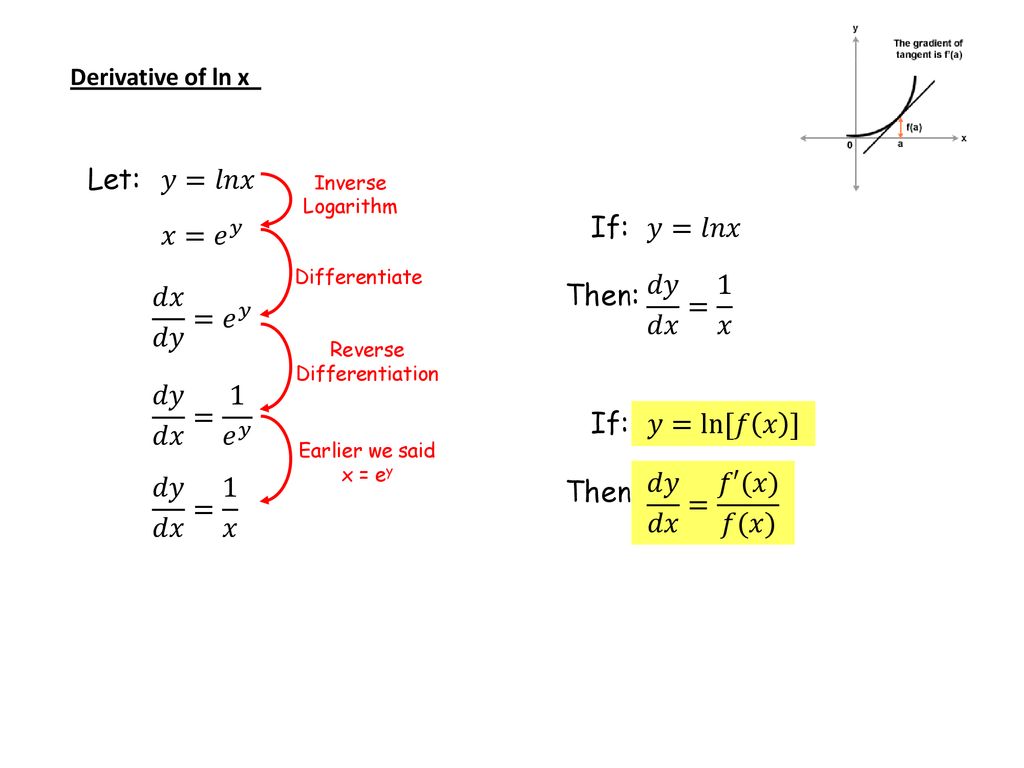



Derivatives Ex Ln X Ppt Download
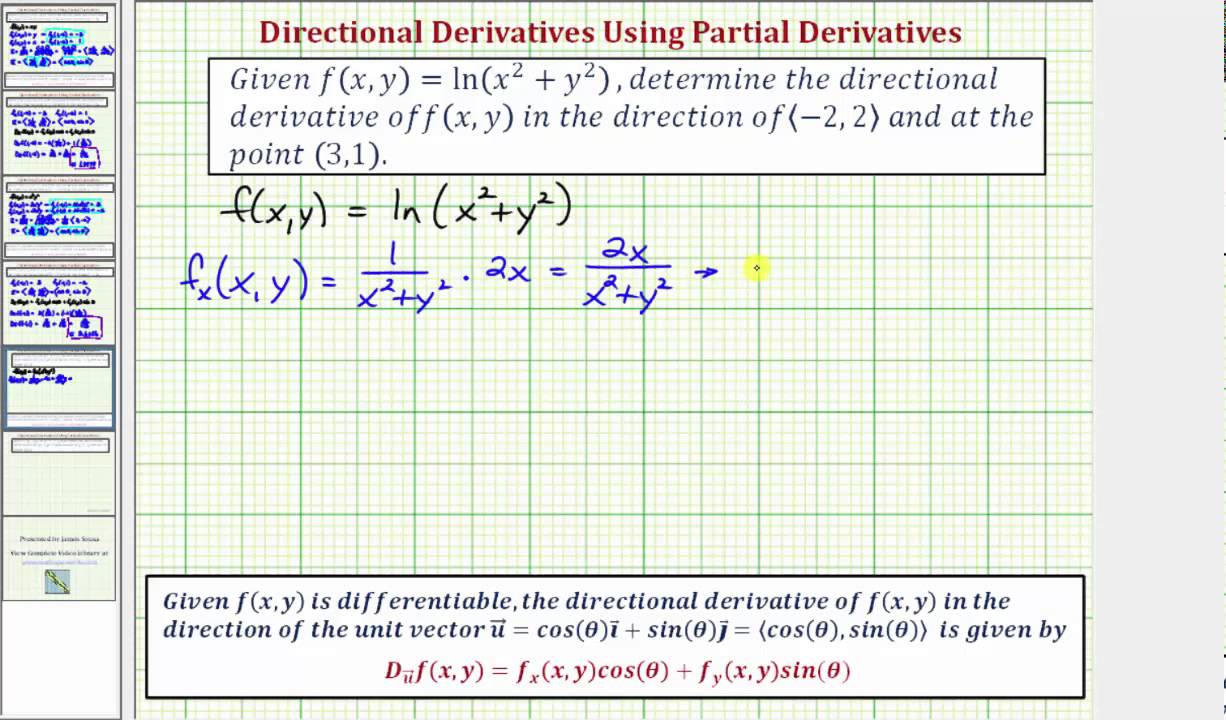



Ex 3 Find A Value Of A Directional Derivative F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Youtube
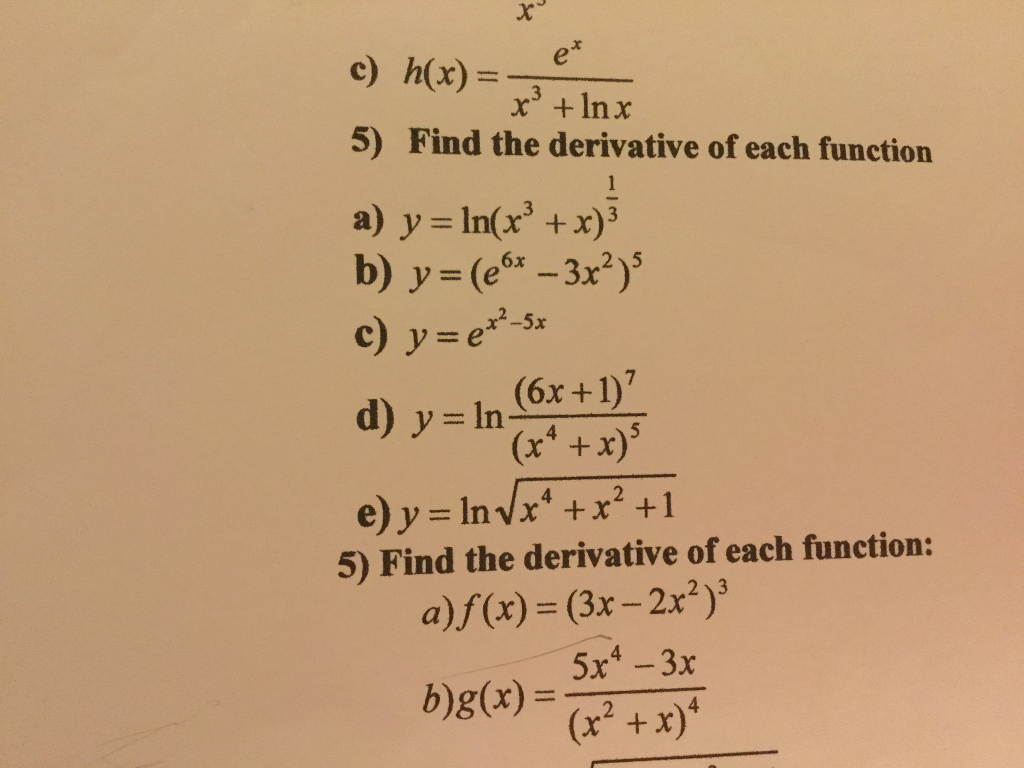



Find The Derivative Of Each Function Y Ln X 3 Chegg Com
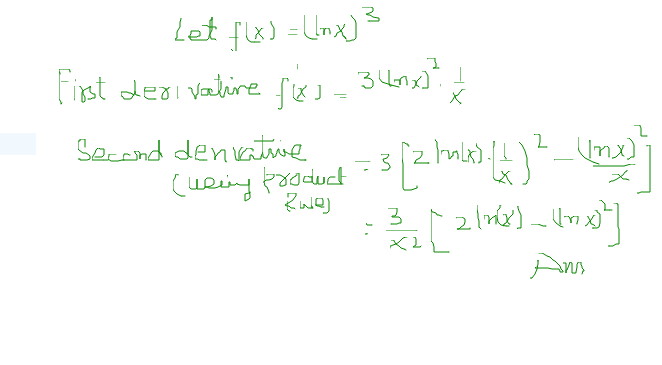



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of Lnx 3 Socratic




Finding The Derivative Of Xln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Solving The Derivative Of Ln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
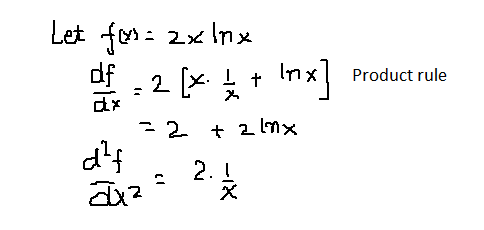



How Do You Find The First And Second Derivative Of 2x Ln X Socratic
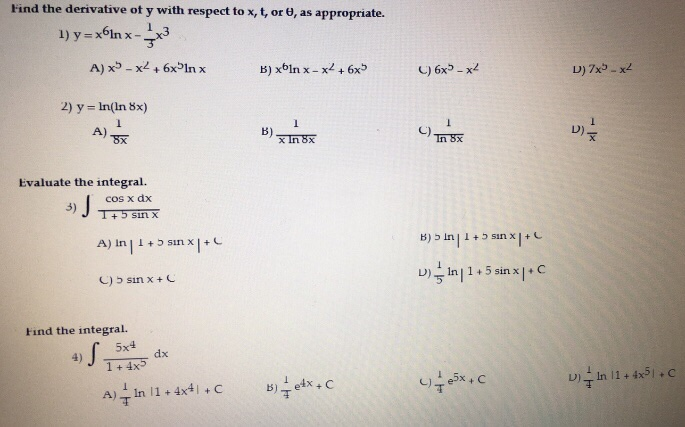



Find The Derivative Of Y With Respect To X T Or Theta Chegg Com




Find The Derivative Of Y 1 Ln X 1 Ln X



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Answered Section 3 6 Derivatives Of Logarithmic Bartleby




What Is The Derivative Of Math E Ln X Math And How Did You Get There Quora




What Is The Equation Of The Tangent Line Of F X Ln X 3 X 7x At X 3 Socratic
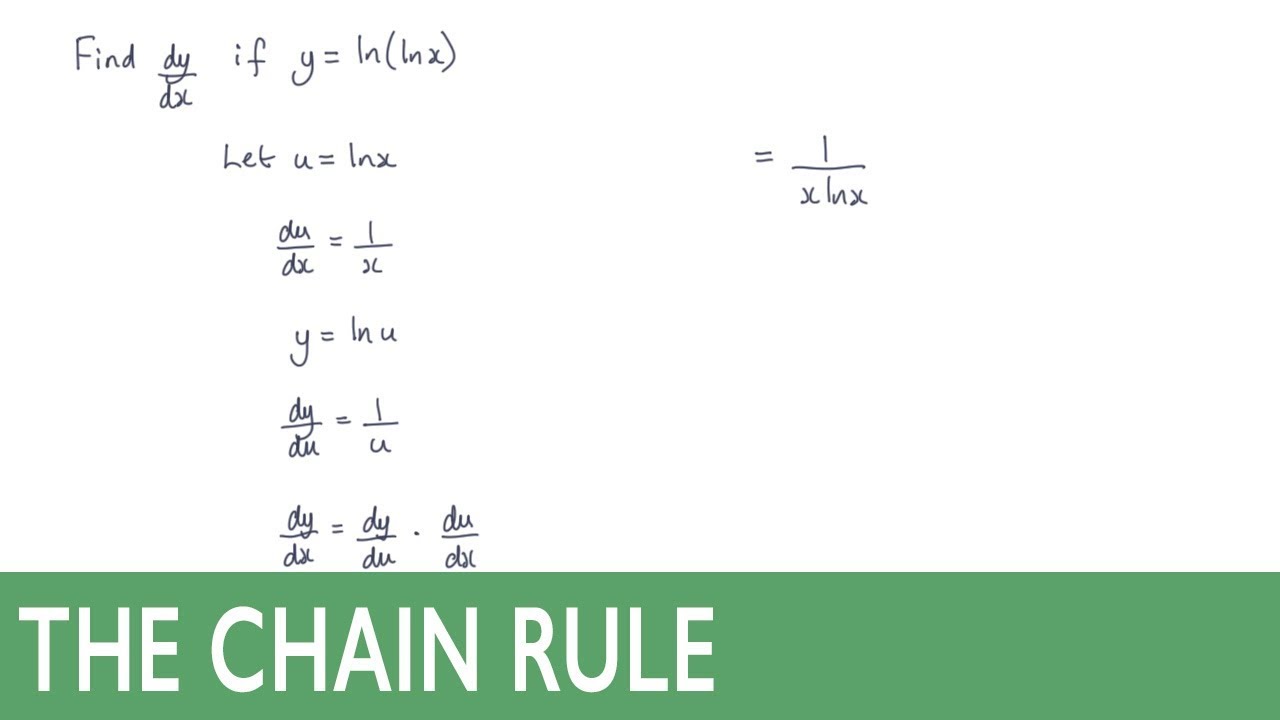



How To Differentiate Y Ln Lnx Using The Chain Rule Youtube
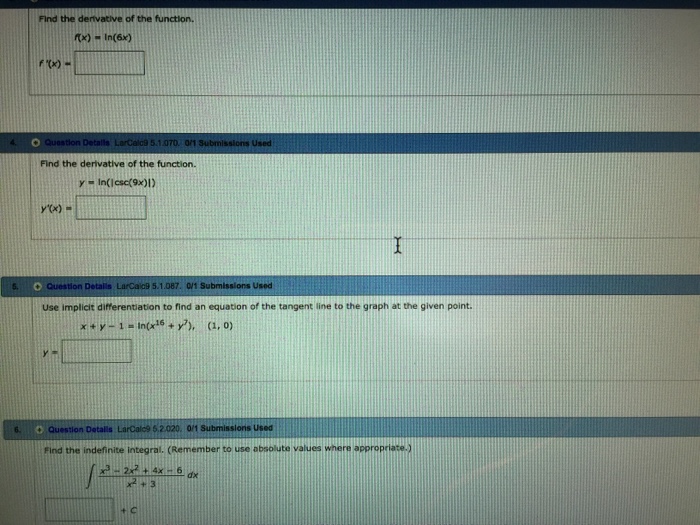



Find The Derivative Of Th Function F X Ln 6x Chegg Com




First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Partial Derivative Math Videos Maths Exam




Compute The Derivative Of Y Ln X 4 X 3 First Chegg Com



Y X Ln X Differentiate The Function Youtube




Solving The Derivative Of Ln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Finding The Derivative Of Xln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
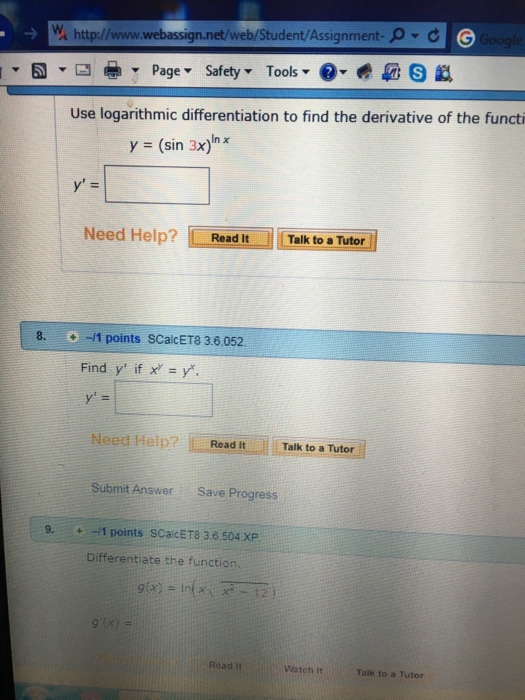



Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find The Chegg Com



What Is The Differentiation Of Ln Sinx Quora



How Do You Determine Whether The Function F X Ln X 2 7 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down And Its Intervals Socratic
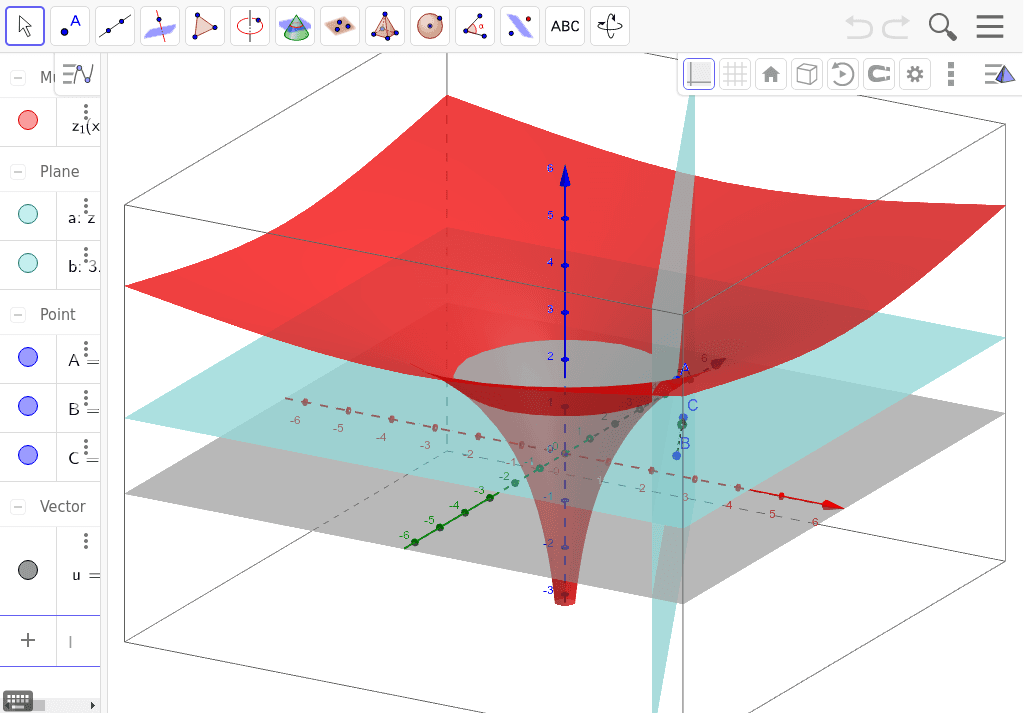



Ln X 2 Y 2 With Directional Derivative Geogebra



Could You Differentiate Sin Y Ln X X 2sin Y Wrt X And Explain Why The Derivative Of 2sin Y Becomes 0 Quora



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function



The Functions Y E X And Y Ln X Youtube
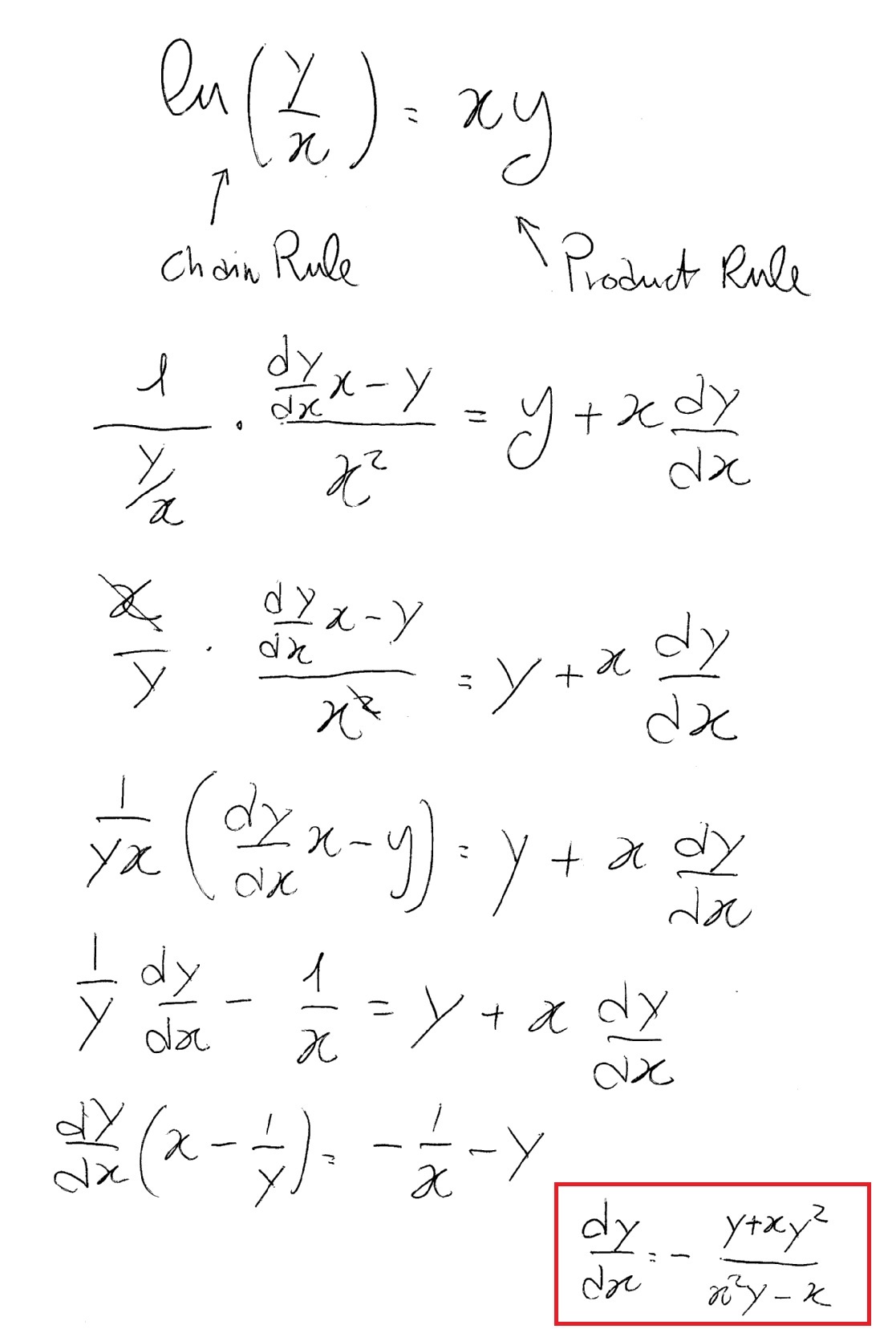



How Do You Differentiate Ln Y X Xy Socratic




Calculating The Derivative Of Ln X 2 Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
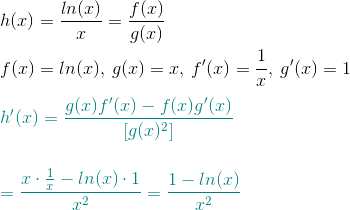



Finding The Derivative Of Ln X X How To Steps Study Com




Derivative Of Ln X Natural Logarithm More
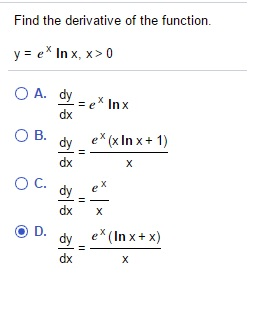



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y E X In X X Chegg Com



7 4 Logarithmic Differentiation




Calculus First And Second Derivative Of Ln X 1 Ln X Youtube




Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange



Find The First Derivative Of Y Y Ln X Squareroot Chegg Com
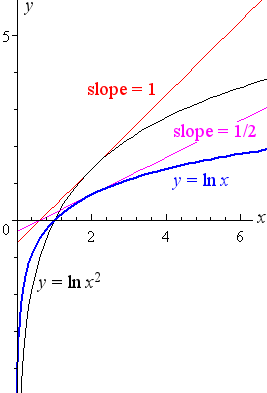



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function




Differentiate X Lnx Using Implicit Differentiation And The Chain Rule Youtube



Lesson 16 Derivatives Of Logarithmic And Exponential Functions
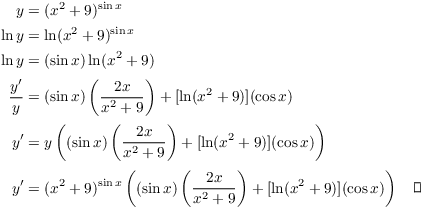



Log And Exponential Derivatives



How Do You Find The Derivative Of Y X Ln X Sin X Socratic
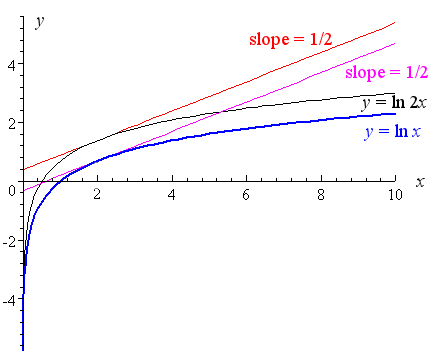



5 Derivative Of The Logarithmic Function
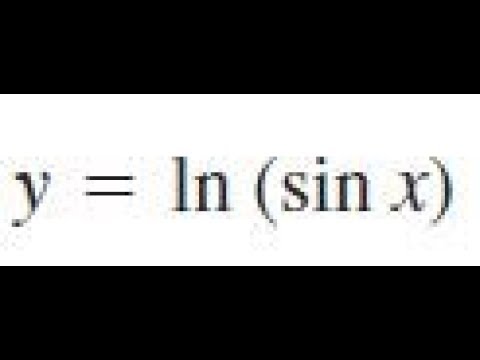



Derivative Of Y Ln Sin X Youtube




Find The Derivative Y Ln X X 6 Y E X 5 Lnx Chegg Com




Solving The Derivative Of Ln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



The Derivative Of Ln X Intuition Proof And Examples




Y Ln X Tan X Use Logarithmic Differentiation To Find Y Dy Dx Youtube




First Order Partial Derivatives Of F X Y Ln X 4 Y 4 Youtube
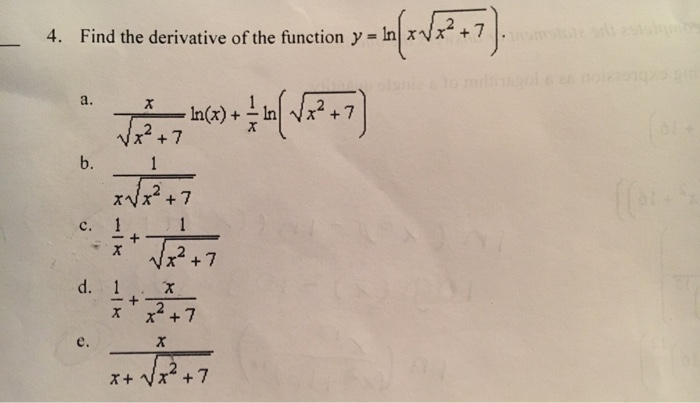



Find The Derivative Of The Function Y Ln X Chegg Com




How To Find Dy Dx When Ln Xy X Y Quora



Logs And Derivatives
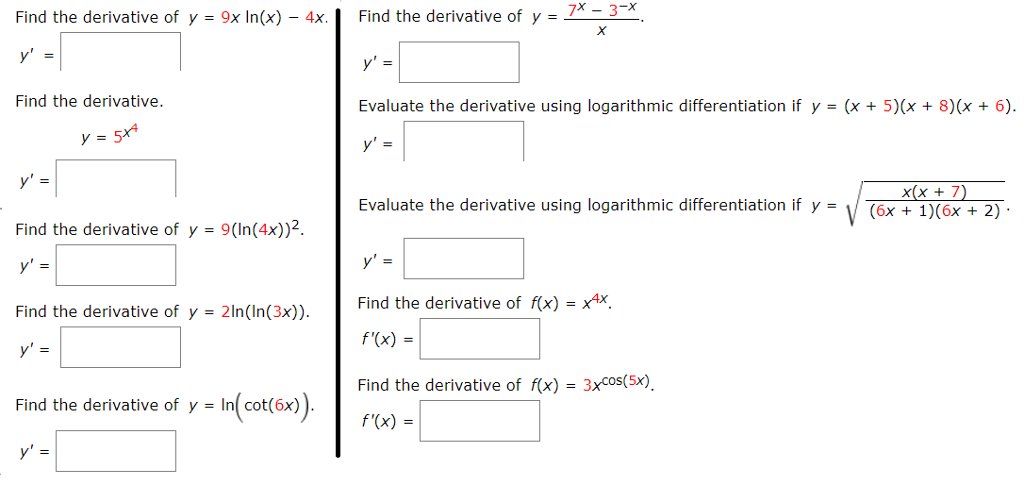



Find The Derivative Of Y 9x Ln X 4xj Y Find The Chegg Com




Derivative Of Y Xlnx X Youtube




Finding The Derivative Of Xln X Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
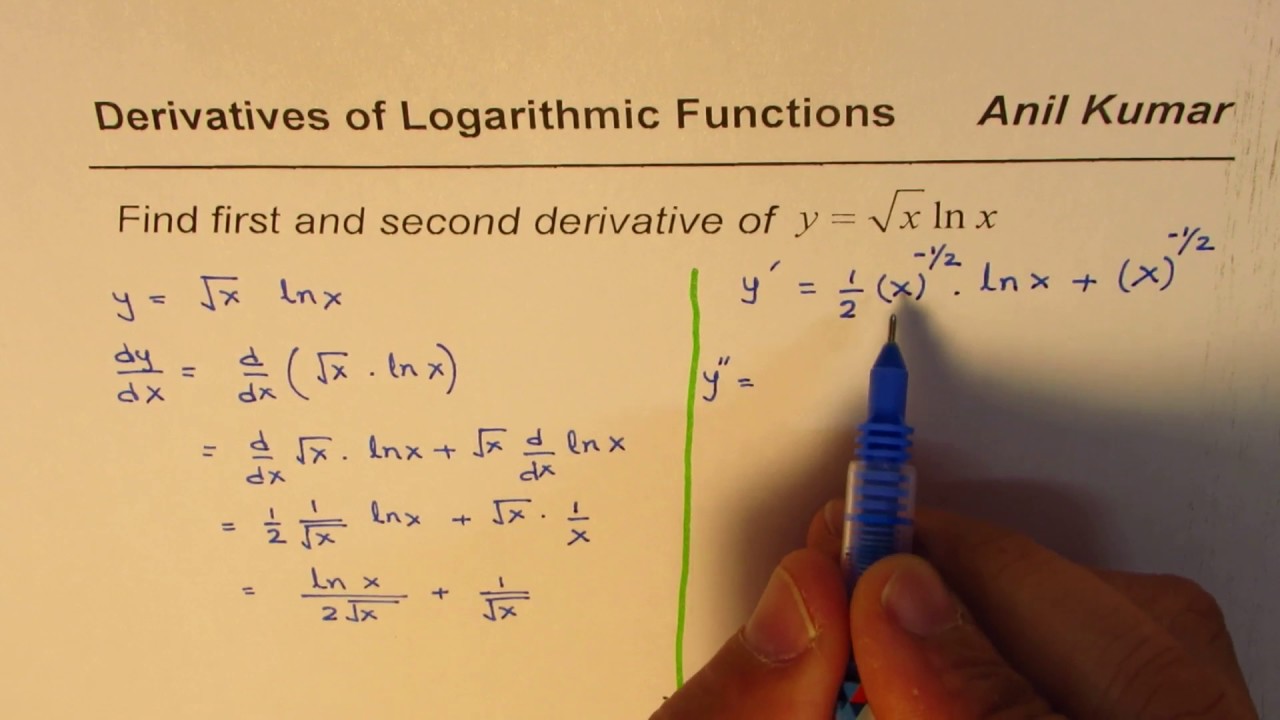



First And Second Derivative Of Sqrt X Ln X Youtube
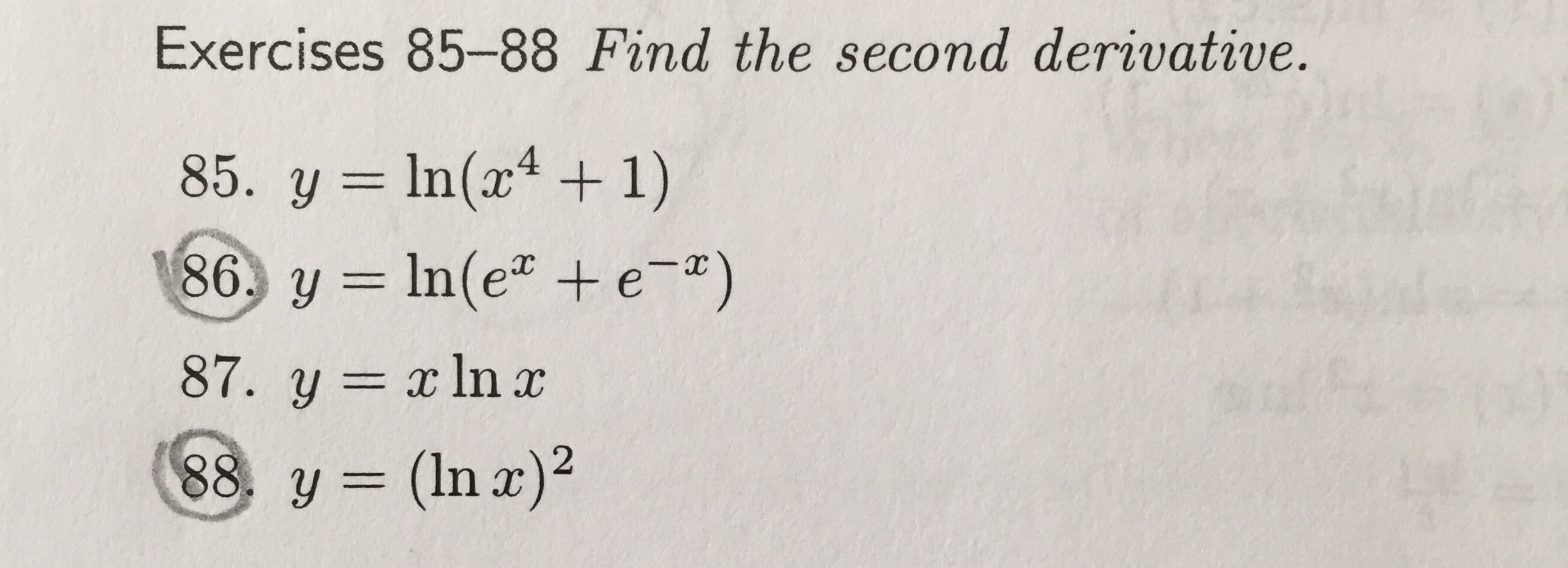



Exercises 85 Find The Second Derivative Y Chegg Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿